What Are Zero-Click Searches?
Zero-click searches are defined as search queries that users input within Google (or any other search engine) that don’t lead to a click on another web property.
As a user yourself, it’s likely you perform zero-click searches more than you realise. For instance, remember the last time you looked up a business’ opening hours? You were likely served a Google My Business listing with all their opening hours available at the top of search. And, when was the last time you asked a question only to have the answer sitting right at the top of the results page? In both scenarios, a journey through to a website simply isn’t required.
Zero-Click Data in 2021
In March, Rand Fishkin, the founder of Sparktoro published updated research on zero-click searches in 2021. He claimed:
“From January to December, 2020, 64.82% of searches on Google (desktop and mobile combined) ended in the search results without clicking to another web property.”
He also claimed in his research that 46.5% of searches were zero-click on desktop, and 77.2% were zero-click on mobile devices. The data he used for his analysis was from SimilarWeb, which was formed of a pool of 5.1 trillion worldwide Google searches.
Google’s Response to the Data
Google refuted these claims shortly after Rand Fishkin’s publication of his data, stating:
“As practitioners across the search industry have noted, this claim relies on flawed methodology that misunderstands how people use Search. In reality, Google Search sends billions of clicks to websites every day, and we’ve sent more traffic to the open web every year since Google was first created. And beyond just traffic, we also connect people with businesses in a wide variety of ways through Search, such as enabling a phone call to a business.”
The two sides of the argument have led to a lot of debate in the search world, with Contributing Editor to Search Engine Land, Barry Schwartz stating:
“There is absolutely no way that 65% of all searches do not lead to a click to a website. But even if that is true, those clicks can lead to driving directions to your local restaurant for curbside pickup or those clicks can lead to a tap on a phone number to call the local hardware store to find out what supplied to order to fix the leaky sink in the house.”
He summarised by saying that we shouldn’t take the study or Google’s response at face value.
So, what can we take from this recent controversy with zero-click data? Well, we know that zero-click searches do happen, no matter their frequency, so we need to continually consider how we can best serve our audience the appropriate information – onsite or in the search results.
What Contributes to Zero-Click Search?
When Google responded to the Sparktoro data, they explained that there are a number of reasons that users don’t click onto a website in the search results after a search, these reasons they mentioned include:
People Reformulate Their Queries
Google explains that people naturally refine their searches when they don’t get the results they anticipated. An example of this would be a user performing a broad search for ‘trainers’. They may find that when they see the results, they wish to modify it further to ‘white trainers’ as there is too much choice to click on a result. Once they modify their search to get the results they want, they are far more likely to click through to a website.
People Look for Quick Answers
People want answers quickly, so when a simple query is performed like a weather forecast, a translation or a currency conversion, Google will show the information directly in the search results. This means that the user has their information and doesn’t necessarily need to click through for more.
People Connect with a Business Directly
Thanks to Google My Business listings and Google Maps, business’ key contact information and opening hours are displayed in the search results. This means that a user can get a telephone number, directions or opening times for your business without having to visit your website.
People Navigate Directly to Apps
If users have a relevant app on their phone that correlates with their search query (e.g., Netflix or Amazon), the links will take them straight to the app instead of the website. This can count as a zero-click search.
Google SERP Features That Contribute to Zero-Click Search
Google incorporates a number of SERP features that contribute towards zero-click search. For example, if you are looking for directions to a business, a click through to their map location via Google My Business still counts as a zero-click search, as they are not journeying onto your website. Some SERP features do include links to websites (e.g., Google My Business and featured snippets), but often the question has already been answered by that point.
Knowledge Panel
The Knowledge Panel shows for a variety of queries in the search results. On desktop, it shows on the right-hand side of your screen, and provides information on businesses, people, animals, countries and more.
Local Panels
These are panels that Google shows for local businesses. To help increase the chances of your business showing here, you need to create a Google My Business account and verify your business. Google will determine whether it shows the panel or not by taking into consideration relevance, distance, and the prominence of your business.
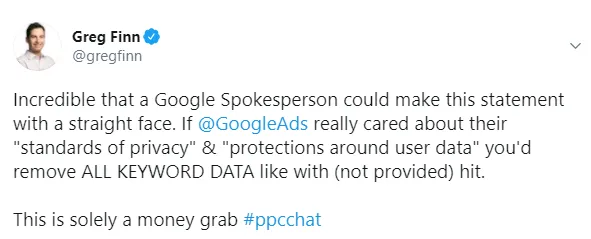
Branded / Personal Panels
Brand and personal panels are not self-created, Google decides itself whether a panel shows for a brand or person. Generally, if there is a Wikipedia page for the brand or person, then there will be a knowledge panel showing for them.

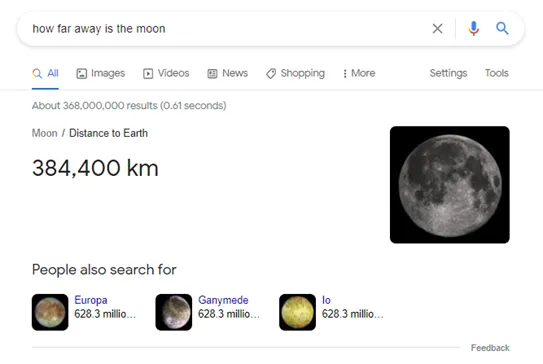
Answer Box
Google’s direct answers box is different from its featured snippets box in that the answers it gives here are facts from Google’s own data sources. There are no links to third party websites in the direct answer box, just the answer itself.
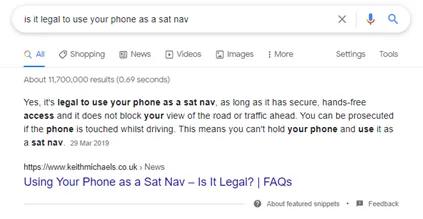
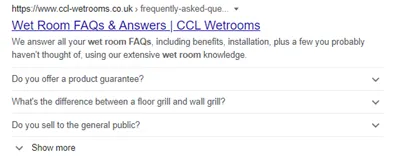
Featured Snippets
Featured snippets, a bit like direct answers, give users an answer directly in the search results. The main difference is that the content is pulled from a third-party website, and a link to the source is directly underneath, giving them an option to click through for further info. These can display as text featured snippets, tables, lists and videos.
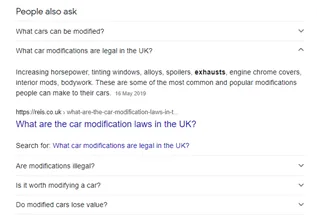
People Also Ask Box
The People Also Ask box displays a number of related questions and answers to the search performed in Google. These can give an answer directly on page, a bit like featured snippets. They also offer a link to the third-party website for more information.
Rich Features
Schema markup can enhance snippets in the SERPs to display an array of additional information. From how-to schema which shows the steps required to action something to FAQ page schema which can display questions and answers below your snippet. All of these different available features have the opportunity to answer a user’s question without them needing to click through to a website.
Is Zero-Click Search a Problem?
In our opinion? No. Improving user experience should never be seen as a problem. If you need opening hours for a business, would you rather get the answer after one step or two steps? If you wanted the date of a historical event, would you rather have the date right there at the top of search or would you be content with scanning through Wikipedia until you found it?
If you think about it, zero-click search is likely to contribute towards lowering overall bounce rate and improving average session duration, as people can get their quick bit of information without needing to click onto your site and leave.
Search is always evolving, and rather than pushing against it, we should be looking to adapt to the changes. However, though we don’t see zero-click search as a bad thing, that’s not to say that you should sit back and do nothing about it.
Adapting to Zero-Click Search
There are a number of things you do to adapt to zero-click search.
1) Optimise for Featured Snippets
Are you making the most of featured snippets? The beauty of gaining these is that your website can outrank competitors hogging the top spots. If your keywords are ranking anywhere on the first page of search, and the query itself shows a featured snippet at the top of SERPs, you have the opportunity to steal that spot. Follow our handy guide for the specifics on how to target featured snippets. Being right at the top of the search results with a featured snippet gives users the option to click through to your website for more information.
2) Make Sure You Set Up and Verify Your Google My Business Profile
Google My Business is critical for local SEO, it’s your hub for all your local contact details, reviews, opening hours and location. It also means that if someone searches for your business on Google, your business is more likely to show in the Knowledge Panel. If someone wants your phone number quickly, or wants to check your closing time, they can easily check your Google My Business profile without having to go to your website.
3) Form a Careful Keyword Strategy
You want the right people to come onto your website. When considering and developing your keyword strategy, you’ll want to consider a combination of action-led keywords and longer tail keywords that can’t easily be answered by Google in the SERPs (i.e., a query that needs a lengthier explanation). A careful keyword strategy that considers intent will ensure that you’re driving the right users to your website, whilst still satisfying those who want a quick answer (incorporating conversational and first-person searches).
At the end of the day, Google favours sites that best meet their audience’s needs. To ensure you’re doing this, you need to consider the different stages of the buying cycle, and how your audience will be searching during these different stages (e.g., ‘should I buy an electric car?’ vs ‘buy tesla model 3’.)
4) Make Use of Schema for Rich Features
For users who want supplementary information, and to prevent wasted clicks to your website, you can display extra information in your search snippets. For instance, by utilising product schema, you can show price and availability in the search results. If this info satisfies the user, they can then click through to the site, if it doesn’t, they can move on.
Additionally, you can help users looking for quick answers to their questions or guide them on how to perform an action purely in the SERPs with FAQ Page and How-To schema. Follow our guide to schema markup for detailed instructions.
Looking For Further Guidance With SEO?
Our SEO specialists can help. Discover more information about our SEO services and drive business growth.






